Internet Research Project
Privacy Risks in Data Collection and Storage
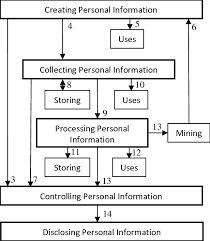
The collection and storage of personal data have become integral to many online services, but they also present significant risks. Organizations collect vast amounts of user data for targeted advertising, analytics, and service improvements. However, improper data handling can lead to security vulnerabilities, exposing users to privacy breaches.
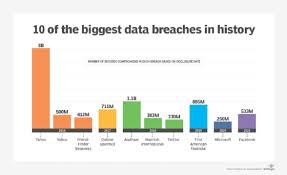
One major risk involves unauthorized data access through cyberattacks. Data breaches at companies like Equifax and Facebook have exposed millions of users’ personal information, leading to identity theft and financial fraud. Weak encryption practices and improper access controls often contribute to these breaches.
To mitigate these risks, companies implement security measures such as encryption, two-factor authentication, and privacy policies. Governments have also enacted regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) to enhance user data protection and ensure organizations remain accountable for safeguarding personal information.
Example: The Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal.
Misuse and Protection of Computing Resources
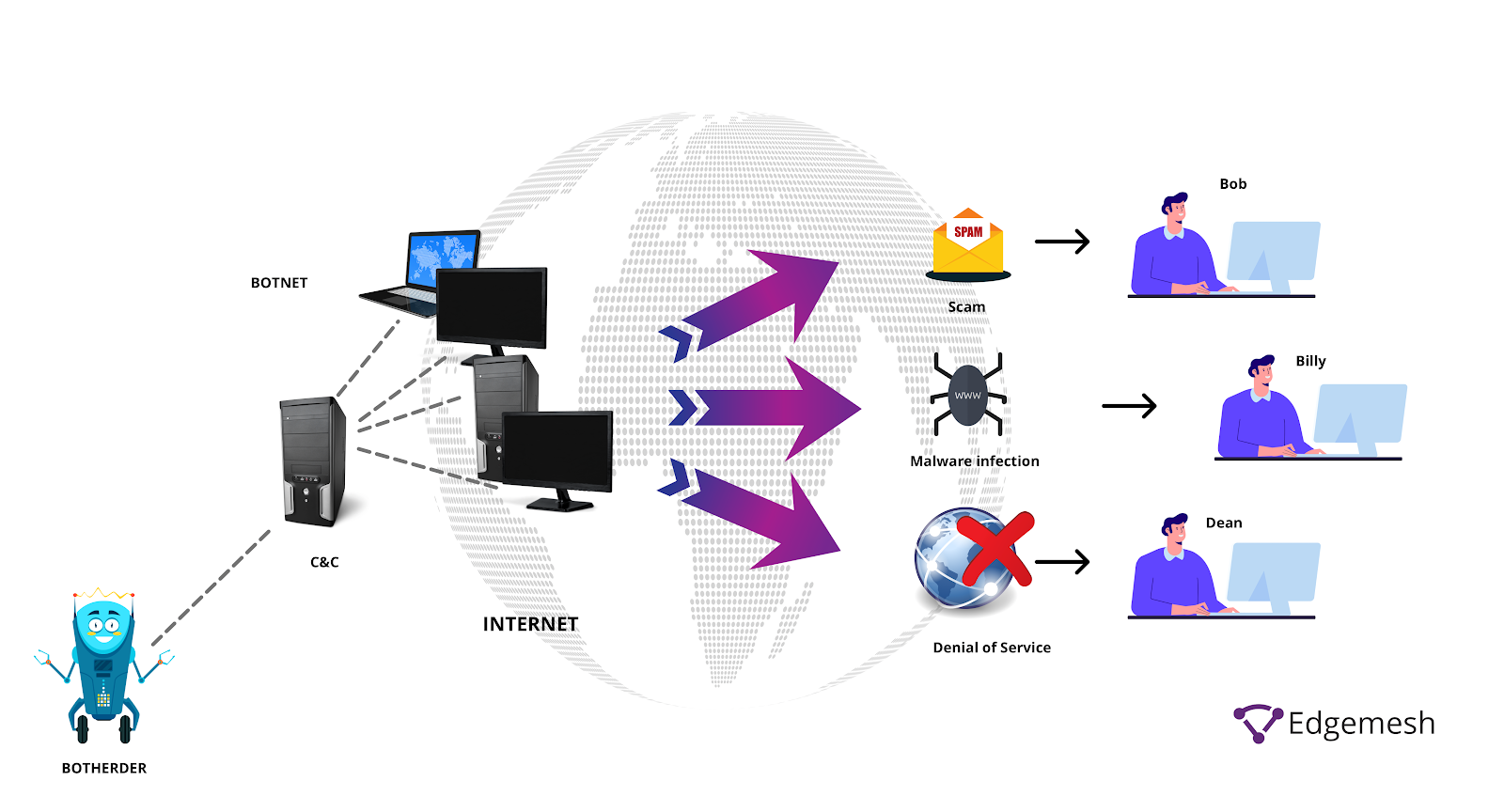
Computing resources can be misused in several ways, including cryptojacking, botnets, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Unauthorized access to processing power and network resources can lead to performance degradation, financial loss, and security risks.
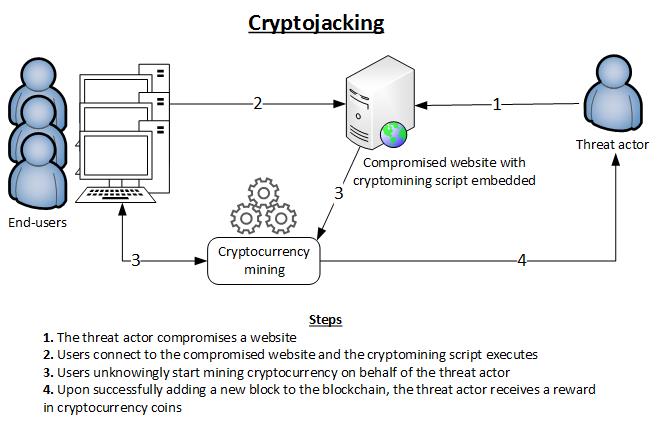
Cryptojacking, for example, is a type of cybercrime where hackers exploit users' computing power to mine cryptocurrency without their consent. This slows down devices, increases energy consumption, and can shorten hardware lifespan. Botnets, which are networks of infected devices controlled by hackers, are often used to launch cyberattacks.
To protect computing resources, organizations implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular system updates. Users can safeguard their devices by installing security software, avoiding suspicious links, and using strong passwords.
Example: Mirai Botnet Attack (2016).
Unauthorized Access to Information

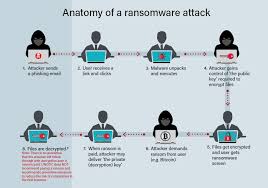
Hackers and malicious actors gain unauthorized access to sensitive information using various methods such as phishing, malware, and brute-force attacks. These attacks can compromise personal, corporate, and governmental data, leading to financial and reputational damage.
Phishing is one of the most common techniques, where attackers deceive users into providing login credentials by pretending to be legitimate entities. Malware, including ransomware, encrypts users' data and demands payment for its release. Brute-force attacks attempt to crack passwords through automated trial-and-error methods.
Cybersecurity measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular password updates, and security awareness training help mitigate unauthorized access threats. Companies also use intrusion detection systems to monitor and block suspicious activity.
Example: Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021).
Benefits and Risks of Computing Innovations
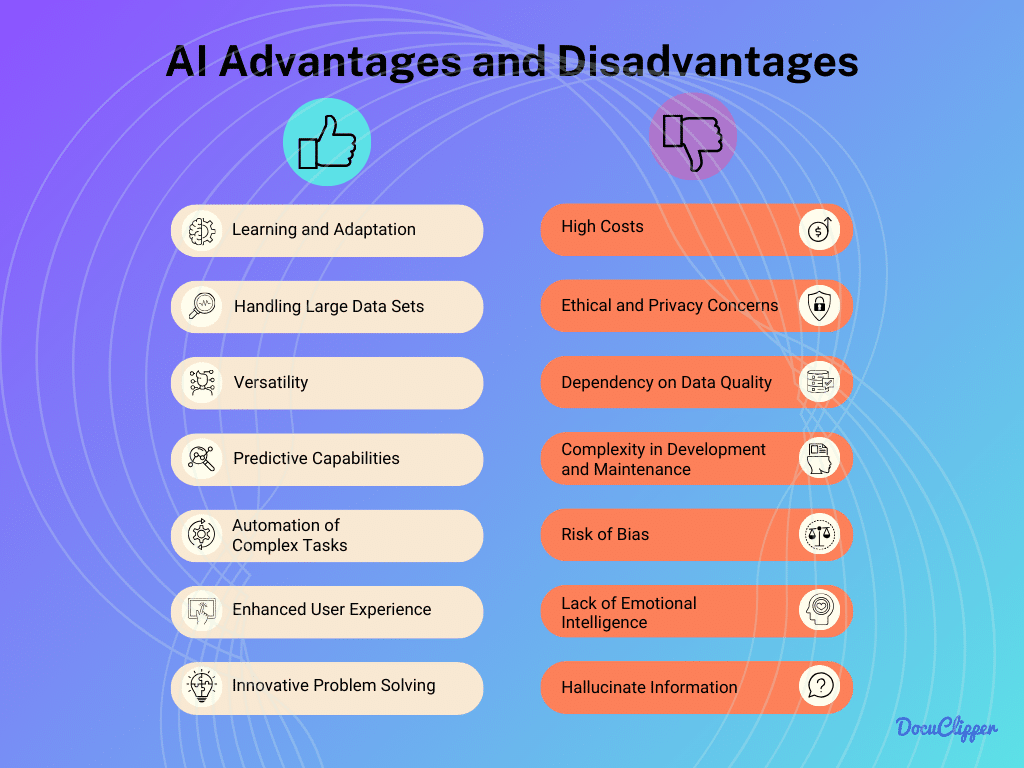
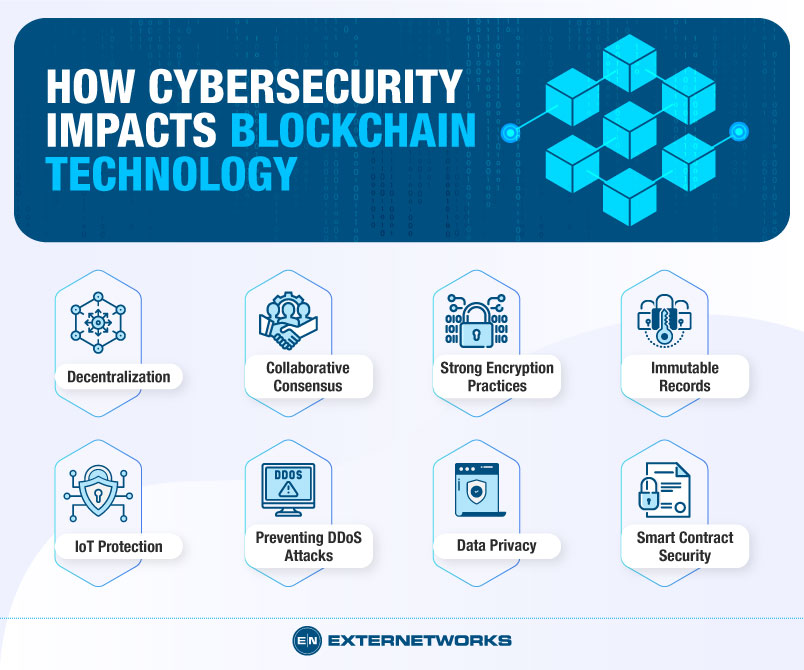
Computing innovations have transformed industries and everyday life, but they also present unintended risks. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and cloud computing offer efficiency, automation, and security benefits but can also lead to job displacement, privacy concerns, and ethical dilemmas.
AI-powered automation improves productivity and decision-making in healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. However, it raises concerns about bias in algorithms, surveillance, and the ethical implications of autonomous systems. Blockchain enhances security and transparency but can be misused for illicit activities, such as money laundering and tax evasion.
Balancing the benefits and risks of computing innovations requires ethical considerations, robust regulations, and ongoing technological improvements to ensure responsible use.
Example: Facial Recognition Technology.